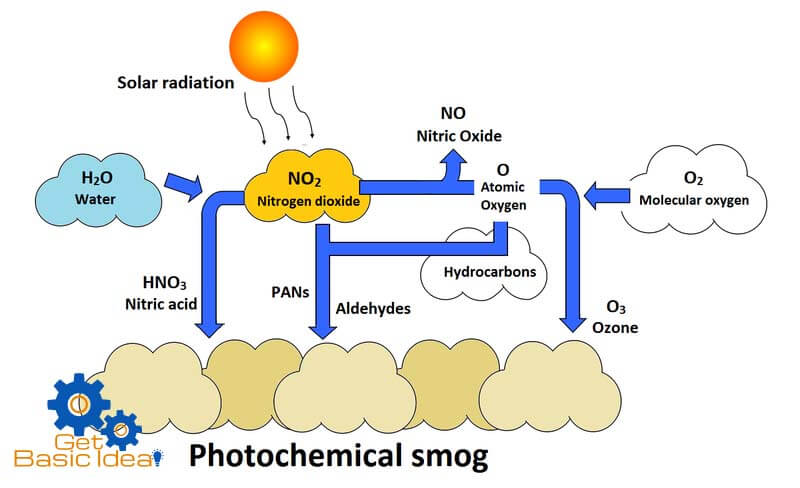
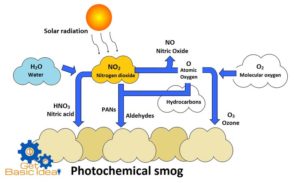
A smog is a combination of smoke and fog. The initial reaction of photochemical smog is the photolysis of nitrogen dioxide (NO2) into nitrogen (NO) monoxide and ozone (O3).
[g_article_ads]
Nitrogen dioxide is found in the exhaust gases given out from automobiles and industries. This NO2 dissociates in the presence of UV radiation emit with the sunlight.
The free oxygen atoms produced rapidly reacts with oxygen gas in the atmosphere to produce ozone. Ozone is a photochemical oxidant having strong oxidizing properties. O3 is also produced when operating the photocopiers and laser printers. O3 generated in this manner further reacts with NO producing more NO2 and O atoms. This NO2 starts the above cycle again.
The unburnt hydrocarbons can react with atomic oxygen to produce variety of aldehydes and ketones. These along with ozone and nitrogen dioxide react to generate series of compounds collectively known as peroxyacyl nitrates (PAN) and peroxybenzyl nitrate having tear gas like properties in the presence of free radicals. Hydroxyl free radicals and other organic fragments having unpaired electron initiate the chemical reactions to form above compounds. As the result of all above chemical reactions a yellowish brown color smog can be seen in the atmosphere. This incident is known as “Photochemical smog”.
Impacts of photochemical smog.
- Adverse effects on human health and sanitary :
Photochemical smog can cause irreversible damage on lungs and heart. Painful irritation of respiratory system reduced lung function and difficulty of breathing, coughing, wheezing asthma and irritating eyes are common effects. Some compounds containing in the smog are carcinogenic. - Causes problems for plants and other animals :
Can interfere with the growth and the productivity of the trees. It can reduce the growth and photosynthesis of plants. - Ozone present in the smog can damage some materials :
Can cause cracking of rubber, reduce the tensile strength of textiles, cracking of paint, fading of dyes and can damage valuable artworks and books. - Visibility problems.
[g_article_ads]
Admin of Get Basic Idea / Senior Solution Architect.